|
|
What is HDMI?
HDMI - short for High Definition Multimedia Interface - is a video connection standard and cable type for carrying high definition video and surround sound audio to televisions, monitors, and projectors. Since its introduction in 2002, it has become the de facto standard in the entertainment sector. It is ubiquitous on TVs, projectors, game consoles, computers, video players, and streaming sticks.
|
|
 |
|
|
HDMI ports and connectors |
|
The most common HDMI port is the original HDMI Type A connector, a 19-pin, 13.9mm x 4.45mm connector used on virtually all mainstream consumer electronics equipment. When space is a constraint - like on tiny microcomputers or DSLR cameras - the HDMI Type C (mini HDMI) and HDMI Type D (micro HDMI) connectors might be used instead.
|
 |
HDMI (Type A)
|
|
 |
mini HDMI (Type C)
|
|
 |
micro HDMI (Type D)
|
|
|
|
HDMI through the years |
|
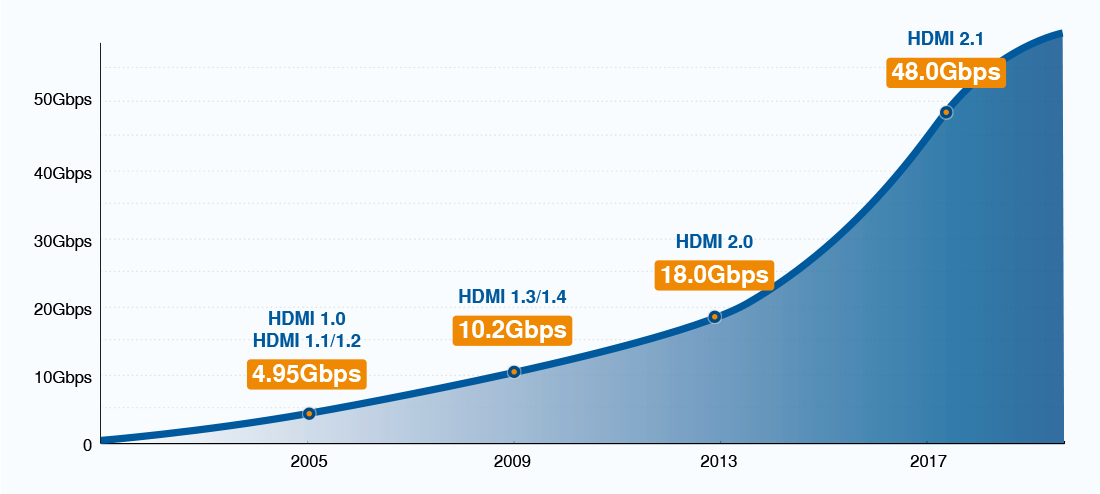
When HDMI first debuted in 2002, the consumer electronics industry was beginning the transition to high definition. HDMI 1.0 only offered enough bandwidth for a 1080p display, but successive generations of HDMI significantly upped bandwidth and resolution limits. HDMI 2.0 reigned supreme for many years with 4K video support to match the transition to 4K in the 2010s.
|
Bandwidth |
 |
|
HDMI cables that support older HDMI standards are still available, although you won't be able to take advantage of new HDMI features like 8K video. You'll find these cables advertised as "4K" HDMI cables.
|
|
|
|
|
|
HDMI 2.1: The future of video |
 |
|
HDMI 2.1 - the latest and greatest HDMI connector standard - brings HDMI's bandwidth, resolution, and refresh rate support to new heights. With 48Gbps of bandwidth, HDMI 2.1 supports near-lifelike 8K video and a host of media-centric features to take entertainment to the next level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
HDMI 2.1 gaming |
 |
|
While 8K televisions aren't quite mainstream yet, HDMI 2.1 shines as the perfect gaming connector. It supports ultra-fast 4K 120Hz high-end televisions for ultra high resolution, tear-free graphics. Combined with gaming-focused features, it is the perfect choice for the latest generation of game consoles.
|
|
|
|
|
|
HDMI features |
|
HDMI doesn't just carry video and audio signals. It also offers a wide array of entertainment and performance features to do more and simplify the home theater experience.
|
 |
Enhanced Audio Return Channel
Enhanced Audio Return Channel (eARC) simplifies your home theater setup by carrying audio signals from your HDMI-connected equipment to a soundbar or audio receiver. Learn More
|
|
 |
Dynamic HDR - High Dynamic Range
Dynamic HDR creates lifelike pictures with stunning color accuracy, depth, and brightness. HDR provides a wider color gamut and expanded brightness options for true-to-life visuals. Learn More
|
|
|
 |
Display Stream Compression
Display Stream Compression (DSC) is a form of visually lossless compression for ultra high definition displays. DSC further ups the resolution and refresh rate support of HDMI 2.1 beyond 8K, ensuring it will remain a relevant and capable cable standard for years to come. Learn More
|
|
 |
Variable Refresh Rate
Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) is a new HDMI 2.1 feature that dynamically adjusts a display's refresh rate to reduce or eliminate lag, stutter, and frame tearing. VRR creates more fluid and detailed gameplay.
|
|
|
 |
Quick Frame Transport
Quick Frame Transport (QFT) reduces latency for smooth, lag-free gaming and real-time interactive virtual reality applications.
|
|
 |
Auto Low Latency Mode
Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM) is a new HDMI 2.1 feature that detects when a game console is connected and automatically switches your television to its smoothest, lag-free gaming settings.
|
|
|
|
HDMI cable lengths and active cables |
|
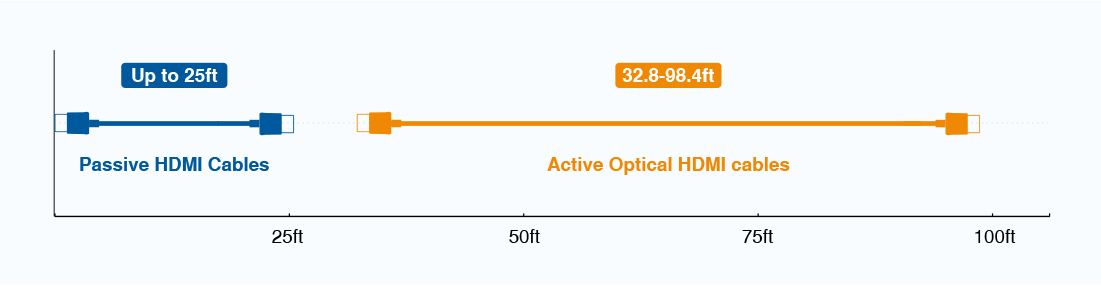
HDMI uses copper cabling to transport video, audio, and data between devices. One downside of this approach is that copper cables can only be so long. Traditional HDMI cables top out at about 25 feet. Active optical cables utilize fiber optics to transport data over longer distances, such as from a projector to an entertainment system. Repeaters combine two standard HDMI cables with a signal booster to preserve data across the entire cable run. Learn More
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
HDMI Ethernet extenders |
|
When even active fiber optic cables aren't long enough, Ethernet can pick up the slack. Specially designed HDMI extenders can convert the signals of an HDMI cable to run over a shielded Ethernet cable. This approach allows for distances of up to 300 feet, but requires a transmitter and a receiver at each monitor.
|
|
|
|
|
|
HDMI matrix switches, splitters, and extractors |
|
Further extend HDMI's versatility with the use of switches, splitters, and extractors. These devices allow one device to output to many HDMI displays - perfect for a storefront, church, or bar.
|
|
|
|
|
|
HDMI vs. USB-C |
|
Both HDMI and USB-C can carry video signals and offer similar performance features, but they differ in form factor and utility. You'll find HDMI ports on large electronics like desktop computers, game consoles, and televisions. USB-C is far more prevalent on mobile electronics like smartphones, laptops, and small form factor PCs.
|
 |
|
Despite these differences, it's simple to convert between the two connectors - you'll just need a USB-C to HDMI adapter. There are plenty to choose from, with new models even supporting 8K video.
|
|
|
|
|
|
HDMI vs. DisplayPort |
|
DisplayPort is the second half of the video connector market. The connector is more common on high-end desktop PCs, computer monitors, and laptops than on televisions or game consoles. Like HDMI, DisplayPort supports 8K video and HDR, though it misses out on some advanced features like eARC and ALLM. Learn More
|
 |
|
Just like USB-C, it is also possible to convert HDMI to DisplayPort. Cable Matters sells a variety of HDMI to DisplayPort adapters and DisplayPort to HDMI adapters suitable for either conversion process.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Resources |
 |
How to connect USB-C to HDMI 2.1? |
|
If you have a brand new 8K TV but your graphics card has a USB-C output, you may be wondering how to connect USB-C to HDMI 2.1. It's easy if you have the right equipment. |
|
|
|
 |
How to: HDMI 120Hz |
|
What do you need to achieve HDMI 120Hz? Depending on your equipment and desired resolution, there are a few ways to push 120Hz through an HDMI Cable. |
|
|
|